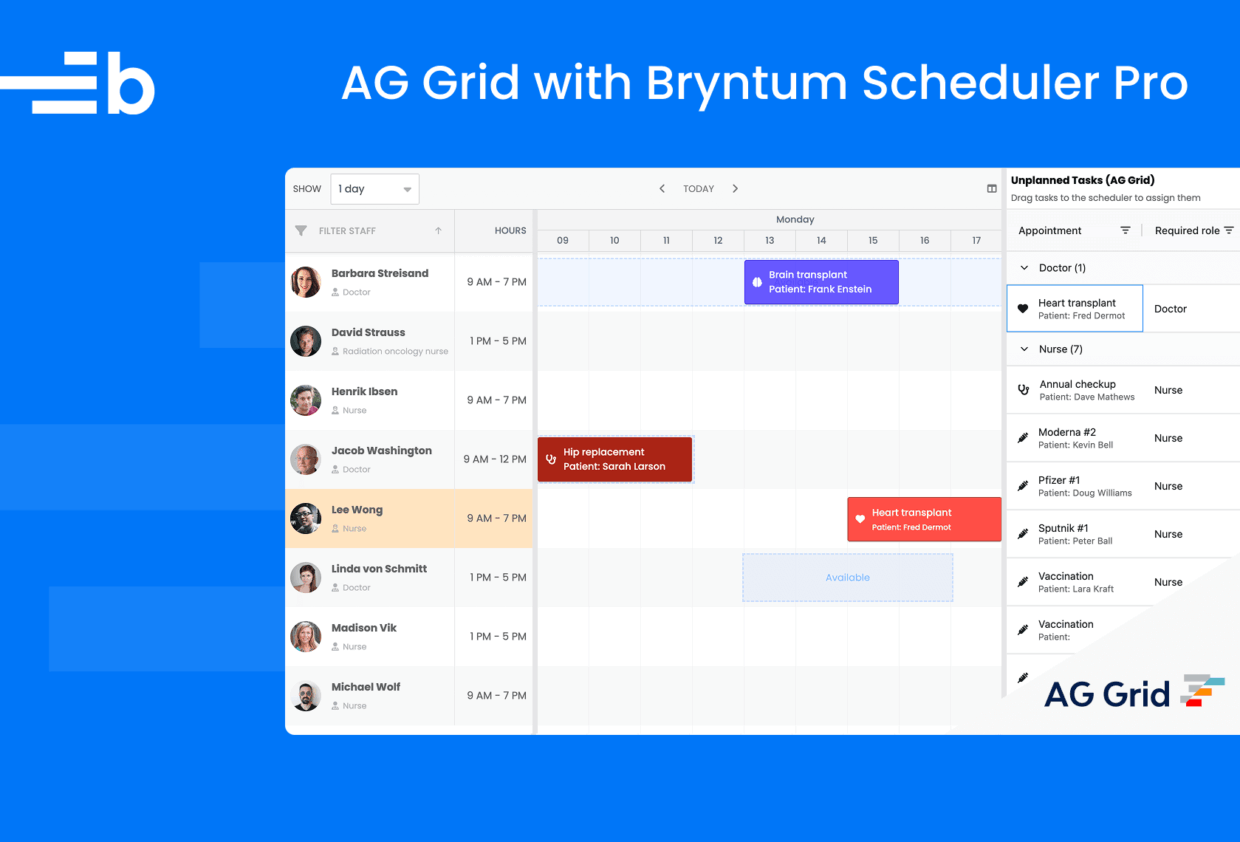
How to integrate a React AG Grid with a React Bryntum Scheduler Pro
Bryntum Scheduler Pro is an advanced scheduling JavaScript UI component for the web. It extends the functionality of the Bryntum Scheduler with additional features allowing you to:
- Use the scheduling engine to automatically schedule events based on their constraints, dependencies, and resource availability
- Display travel times
- Highlight calendars and time spans
- Apply custom event grouping
- Split events into segments
- Add nested events
The customizability of Bryntum Scheduler Pro lets you easily integrate it with other components. A common use case is to set it up alongside a data grid, like in our demo: Drag unplanned tasks from a Bryntum Grid to a Bryntum Scheduler Pro.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to integrate Bryntum Scheduler Pro with AG Grid, a popular JavaScript data grid. Our blog post comparing JavaScript table libraries found that both AG Grid and Bryntum Grid are good choices for feature-rich tables.
We’ll recreate the Bryntum Grid and Bryntum Scheduler Pro demo above, but switch the Bryntum Grid with an AG Grid and connect the app to an Express.js backend to persist the data. We’ll do the following:
- Create a React AG Grid table component.
- Create a React Bryntum Scheduler Pro component.
- Connect the Bryntum Scheduler Pro to an existing Express backend with a local SQLite database.
- Configure the AG Grid to use the Bryntum Scheduler Pro event store.
- Implement drag-and-drop between the AG Grid and Bryntum Scheduler Pro.
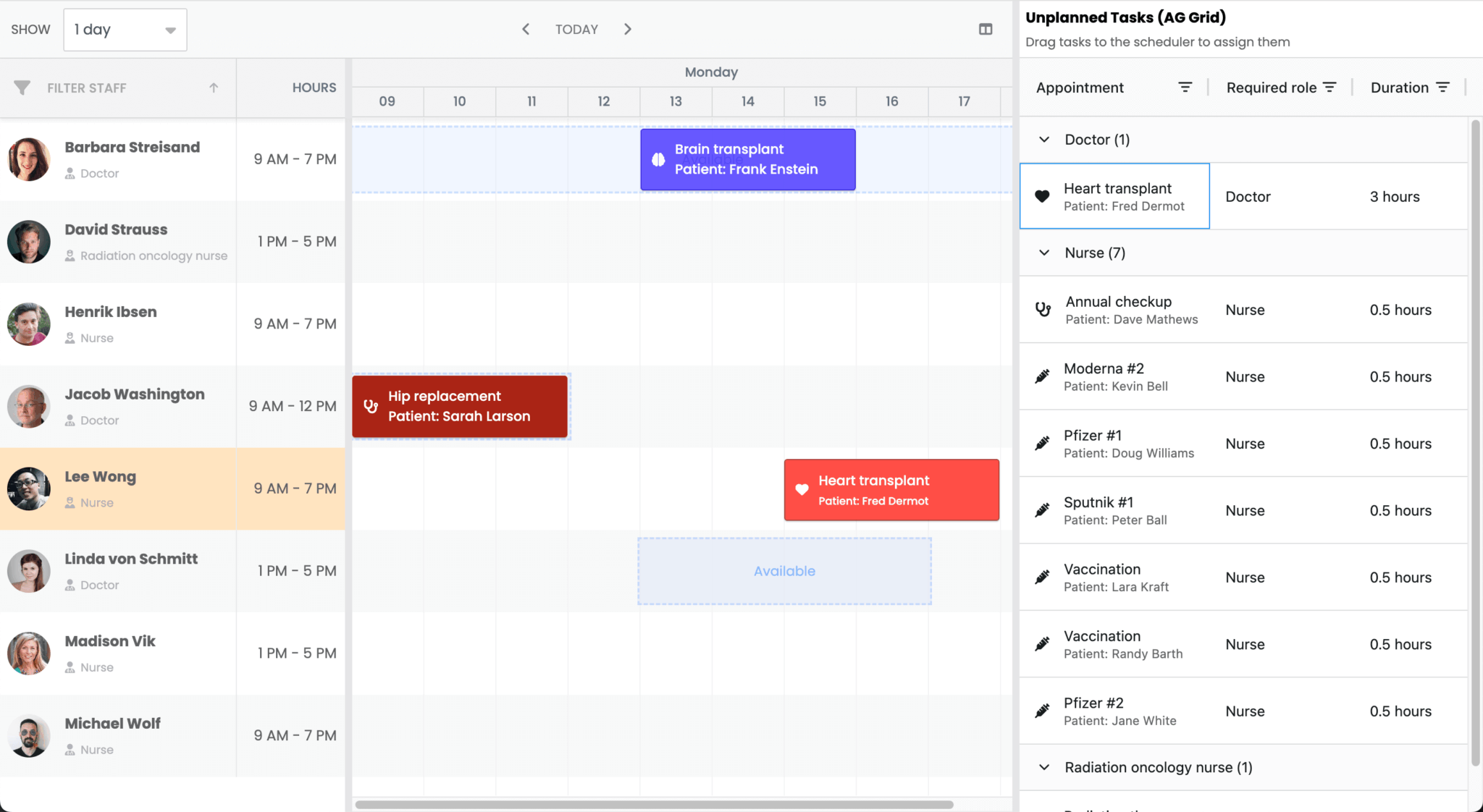
Here’s what we’ll build:
Prerequisites
To follow along, you need Node.js installed on your system.
Getting started
We start with an existing Express backend and a Vite React with TypeScript frontend. Clone the starter repositories:
Install the dependencies for the frontend and backend starters using the following command for each:
npm installThe frontend starter repo has the completed code for this guide on the complete-app branch.
The backend is a working Express server for a Bryntum Scheduler Pro component. It has two API endpoints in the server.js file:
/api/loadfor loading data/api/syncfor syncing data changes
The backend uses a local SQLite database and Sequelize, which is a Node ORM. The example-data folder contains example medical appointment data for seeding the database. There are JSON files for events, resources, event dependencies, assignments of resources to events, and calendars. The models folder has Sequelize data models, which represent tables in the database, for data stores in the Bryntum Scheduler Pro project, where data stores are kept and linked together.
For more details on how the backend was implemented, take a look at our guide to using Bryntum Scheduler with Express and SQLite, which has a similar implementation to the backend used here.
To create the local SQLite database and add the example data, run the addExampleData.js script in the backend:
npm run seedRun the development server for the backend:
npm run devNow that the backend is set up, let’s create the AG Grid and Bryntum Scheduler Pro components.
Create an AG Grid data table React component
There are two versions of AG Grid:
- AG Grid Community is free and open-source.
- AG Grid Enterprise has advanced features.
We use the enterprise version, which you can try out locally without a license key (although the grid displays a watermark and the browser console shows an error message about the license).
Install the AG Grid React component
Install the ag-grid-react package in the frontend project, which also installs ag-grid-community:
npm install ag-grid-reactInstall the ag-grid-enterprise package to use AG Grid Enterprise features:
npm install ag-grid-enterpriseTo minimize the bundle size, only register the AG Grid modules that you’ll use. In the src/main.tsx file, import and register the following AG Grid modules for the purposes of this guide:
import { AllCommunityModule, ModuleRegistry } from 'ag-grid-community';
import { RowGroupingModule, RowGroupingPanelModule } from 'ag-grid-enterprise';
ModuleRegistry.registerModules([
AllCommunityModule,
RowGroupingModule,
RowGroupingPanelModule
]);You can use the selecting modules tool to figure out which modules to import and which registration code you need based on the grid features that you plan to use.
Configure, render, and style the AG Grid
Now we’ll create the main AG Grid component to display unplanned medical appointments. Create a components folder in the src folder. Then, create an UnplannedTasksGrid.tsx file in src/components and add the following code to it:
import { useState, useRef } from 'react';
import { AgGridReact } from 'ag-grid-react';
import { type ColDef } from 'ag-grid-community';
export const UnplannedTasksGrid = () => {
const gridRef = useRef<AgGridReact>(null);
const [tasks] = useState([
{
name : 'Task 1',
patient : 'Patient 1',
requiredRole : 'Doctor',
duration : 1,
durationUnit : 'h'
},
{
name : 'Task 2',
patient : 'Patient 2',
requiredRole : 'Nurse',
duration : 2,
durationUnit : 'h'
}
]);
const columnDefs: ColDef[] = [
{
headerName : 'Appointment',
field : 'name',
flex : 1,
editable : true,
cellClass : 'unscheduledNameCell'
},
{
headerName : 'Patient',
field : 'patient',
width : 120,
editable : true
},
{
headerName : 'Required role',
field : 'requiredRole',
width : 140,
editable : true,
cellEditor : 'agSelectCellEditor',
cellEditorParams : {
values : ['Doctor', 'Nurse', 'Radiation oncology nurse']
},
rowGroup : true,
hide : false
},
{
headerName : 'Duration',
field : 'duration',
width : 110,
editable : true,
cellEditor : 'agNumberCellEditor',
cellEditorParams : { min : 0.5, max : 24, step : 0.5 },
valueParser : (params) => {
const newValue = parseFloat(params.newValue);
return isNaN(newValue) ? params.oldValue : newValue;
}
}
];
const defaultColDef: ColDef = {
sortable : true,
filter : true,
resizable : true
};
return (
<div style={{ width : '100%', height : '100%' }} className="ag-grid-container">
<AgGridReact
ref={gridRef}
rowData={tasks}
columnDefs={columnDefs}
defaultColDef={defaultColDef}
rowHeight={80}
headerHeight={56}
rowGroupPanelShow="never"
groupDefaultExpanded={1}
groupDisplayType="groupRows"
suppressAggFuncInHeader={true}
animateRows={true}
/>
</div>
);
};
UnplannedTasksGrid.displayName = 'UnplannedTasksGrid';The gridRef provides access to the AG Grid API, which we’ll use later. The tasks state holds some initial example tasks data. We define the grid columns using the columnDefs array. The column cells are editable. For the Required role column, we set rowGroup to true to group unplanned tasks by the role they require.
We render the AgGridReact component and add rowData, columnDefs, and other configuration options as props.
Replace the code in the App.tsx file with the following lines of code, which render the AG Grid:
import './App.css';
import { UnplannedTasksGrid } from './components/UnplannedTasksGrid';
function App() {
return (
<div style={{ width : '100%', height : '100%' }} >
<UnplannedTasksGrid />
</div>
);
}
export default App;Run the local development server:
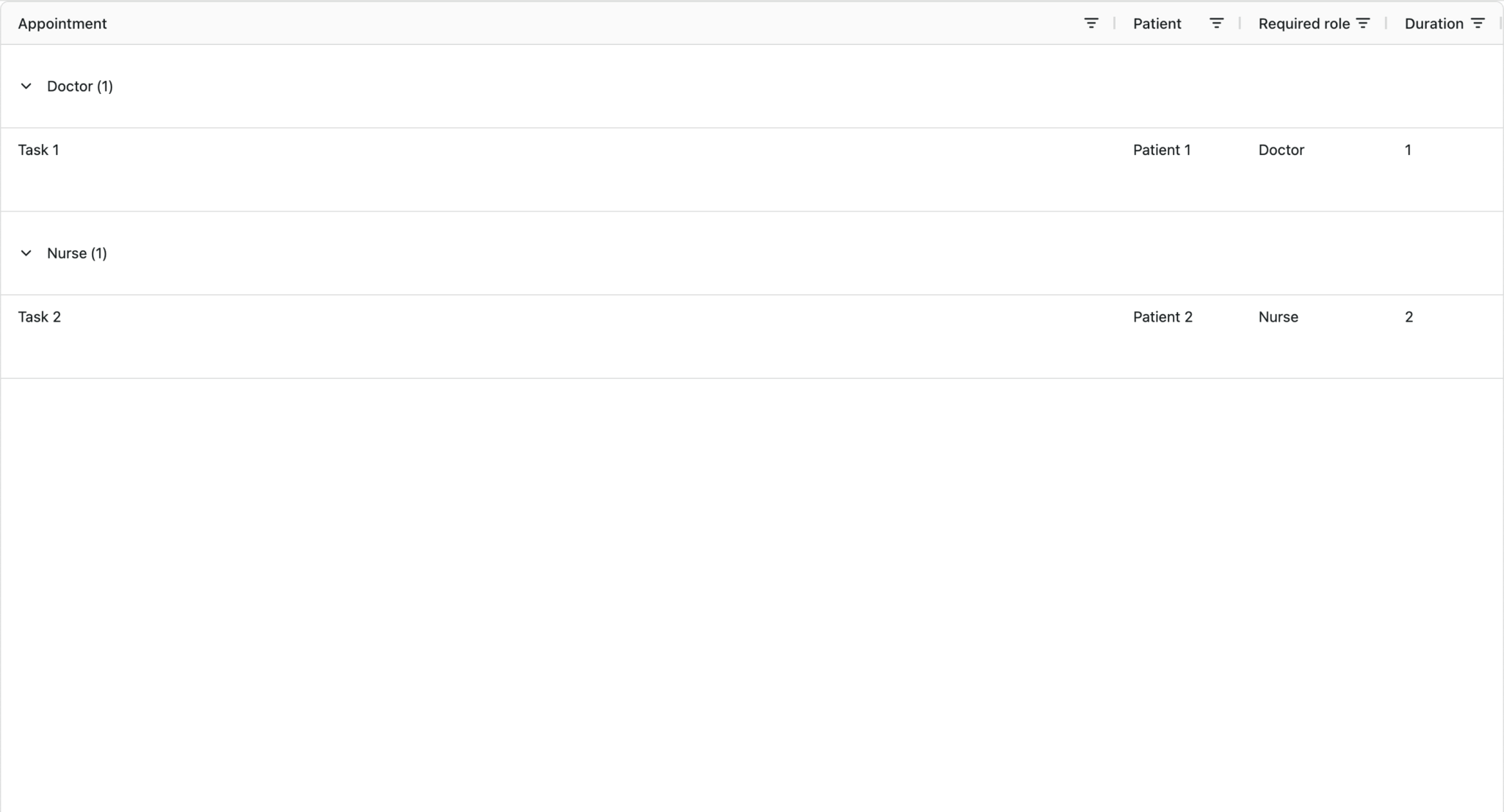
npm run devYou’ll see a basic AG Grid with two tasks:
Now let’s create a Bryntum Scheduler Pro and place it next to the AG Grid.
Create a Bryntum Scheduler Pro React component
First, we’ll install the Bryntum Scheduler Pro. Then we’ll create custom event and resource models, configure the Scheduler Pro, and style it.
Install the Bryntum Scheduler Pro React component
If you’re using the free trial, install the public Bryntum trial packages:
npm install @bryntum/schedulerpro@npm:@bryntum/schedulerpro-trial @bryntum/schedulerpro-reactIf you have a Bryntum license, refer to our npm Repository Guide and install the licensed packages:
npm install @bryntum/schedulerpro @bryntum/schedulerpro-reactCreate custom event and resource models
Before configuring the Scheduler Pro, we need to create custom models that extend the Bryntum base models with our specific medical appointment fields. These models will define the data structure for our appointments and medical staff resources.
First, let’s create a custom Appointment model. Create a lib folder in the src folder. Create an Appointment.ts file in src/lib and add the following lines of code to it:
import { EventModel } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
// Custom Appointment model, based on EventModel with additional fields and changed defaults
export class Appointment extends EventModel {
declare patient: string;
declare requiredRole : string;
declare confirmed: boolean;
static fields = [
'patient',
'requiredRole',
'confirmed',
// override field defaultValue to hours
{ name : 'durationUnit', defaultValue : 'h' }
];
}This custom Appointment model extends the base Bryntum EventModel and includes the medical-specific fields, patient, requiredRole, and confirmed. The fields array defines additional properties beyond the base event fields.
Next, create a custom Doctor model. Create a Doctor.ts file in the src/lib folder and add the following lines of code to it:
import { ResourceModel } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
export class Doctor extends ResourceModel {
declare role : string;
declare roleIconCls : string;
static fields = [
'role',
'roleIconCls'
];
}The Doctor model extends ResourceModel to add the role-specific fields, role and roleIconCls, which allow us to categorize medical staff by their role (such as doctor or nurse) and associate visual icons with each role type.
Configure the Bryntum Scheduler Pro
Now we’ll configure the Scheduler Pro component, which defines the appearance, behavior, and features of the scheduler.
Create an AppConfig.ts file in the src folder and add the following lines of code to it:
import { CalendarModel, DateHelper, type ProjectModelConfig, ResourceModel, SchedulerPro, StringHelper } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
import { type BryntumSchedulerProProps } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro-react';
import { Appointment } from './lib/Appointment';
import { Doctor } from './lib/Doctor';
export const schedulerConfig: BryntumSchedulerProProps = {
startDate : new Date(2025, 9, 20, 9),
endDate : new Date(2025, 9, 20, 19),
rowHeight : 80,
barMargin : 10,
eventStyle : 'border',
eventColor : 'indigo',
allowOverlap : false,
useInitialAnimation : false,
// add path to images
resourceImagePath : 'https://localhost:5173/images/users/',
columns : [
{
type : 'resourceInfo',
text : 'Doctor',
width : 230,
showEventCount : false,
showMeta : (resourceRecord) => {
const { role, roleIconCls } = resourceRecord as Doctor;
return `<i class="${roleIconCls}"></i>${role}`;
},
filterable : {
filterField : {
triggers : {
search : {
cls : 'b-icon b-fa-filter'
}
},
placeholder : 'Filter staff'
}
}
},
{
type : 'column',
text : 'Hours',
width : 105,
editor : false,
filterable : false,
sortable : false,
align : 'right',
renderer : ({ record, grid }) => {
const
scheduler = grid as SchedulerPro,
calendar = (record as ResourceModel)?.calendar as CalendarModel,
ranges = calendar?.getWorkingTimeRanges?.(scheduler.startDate, scheduler.endDate);
if (ranges?.length) {
const range = ranges[0];
return `${DateHelper.format(range.startDate, 'K')} - ${DateHelper.format(range.endDate, 'K')}`;
}
else {
return '';
}
}
}
],
// Custom view preset with header configuration
viewPreset : {
base : 'hourAndDay',
columnLinesFor : 1,
headers : [
{
unit : 'd',
align : 'center',
dateFormat : 'dddd'
},
{
unit : 'h',
align : 'center',
dateFormat : 'HH'
}
]
},
stripeFeature : true,
columnLinesFeature : true,
filterBarFeature : {
compactMode : true
},
calendarHighlightFeature : {
calendar : 'resource',
// This method is provided to determine which resources are available for one or more eventRecords,
// in order to highlight the right availability intervals
collectAvailableResources({ scheduler, eventRecords }) {
const appointment = eventRecords[0] as Appointment;
return scheduler.resourceStore.query((doctor: Doctor) => doctor.role === appointment.requiredRole || !appointment.requiredRole) as ResourceModel[];
}
},
// Configure event menu items with correct phrases (could also be done through localization)
eventMenuFeature : {
items : {
deleteEvent : {
text : 'Delete appointment'
},
unassignEvent : {
text : 'Unschedule appointment'
}
}
},
taskEditFeature : {
editorConfig : {
title : 'Appointment'
},
// Customize its contents inside the General tab
items : {
generalTab : {
// Add a patient field
items : {
// Add a patient field
orderField : {
type : 'text',
name : 'patient',
label : 'Patient',
// Place after name field
weight : 150
}
}
}
}
},
eventRenderer({ eventRecord }) {
return [
{
children : [
{
class : 'b-event-name',
text : eventRecord.name
},
{
class : 'b-patient',
html : StringHelper.xss`<div>Patient: ${(eventRecord as Appointment).patient || ''}</div>`
}
]
}
];
}
};The startDate and endDate set the visible time range for a single day (7 AM to 7 PM), while rowHeight and barMargin control the visual size. The allowOverlap: false setting prevents appointment conflicts.
The columns array defines two main columns:
- The Doctor column displays resource information about doctors, with role icons.
- The Hours column shows working hours.
The viewPreset configures the time axis headers to show the day of the week and hourly intervals.
Several features are enabled, including:
- The
stripeFeaturefor row striping - The
columnLinesFeaturefor visual grid lines - The
filterBarFeaturefor column data filtering - The
calendarHighlightFeaturefor highlighting available time slots based on doctor availability and required roles - The
eventMenuFeaturefor customizing the context menu - The
taskEditFeaturefor customizing the edit dialog for appointments
The eventRenderer function defines how appointments are displayed in the scheduler.
Next, in the same AppConfig.ts file, add the project configuration that handles data loading and synchronization:
export const projectConfig: ProjectModelConfig = {
autoLoad : true,
autoSync : true,
transport : {
load : {
url : 'https://localhost:1337/api/load'
},
sync : {
url : 'https://localhost:1337/api/sync'
}
},
resourceStore : {
modelClass : Doctor,
sorters : [
{ field : 'name', ascending : true }
]
},
eventStore : {
// Unassigned events should remain in store
removeUnassignedEvent : false,
modelClass : Appointment
},
// This config enables response validation and dumping of found errors to the browser console.
// It's meant to be used as a development stage helper only so please set it to false for production systems.
validateResponse : true
};The project handles CRUD operations for the Scheduler Pro. The autoLoad and autoSync options enable automatic data loading and synchronization of changes. The transport object defines the API endpoints for loading and syncing data with the Express backend.
The resourceStore uses the custom Doctor model and sorts resources by name. The eventStore uses the custom Appointment model, with removeUnassignedEvent set to false, to keep unscheduled appointments in the store. We’ll display these unscheduled appointments in the AG Grid.
Render the Scheduler Pro
Add the following imports to the src/App.tsx file:
import { useRef, useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { BryntumSchedulerPro, BryntumSplitter } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro-react';
import { schedulerConfig, projectConfig } from './AppConfig';
import { SchedulerPro } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';Add the following ref, state, and effect hooks to the App component:
const schedulerRef = useRef<BryntumSchedulerPro>(null);
const [scheduler, setScheduler] = useState<SchedulerPro>();
const [toggleLayout, setToggleLayout] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
setScheduler(schedulerRef.current?.instance);
}, [schedulerRef]);The scheduler state will hold a reference to the Scheduler Pro instance and the toggleLayout state will control whether the layout displays the grid and scheduler side by side or stacked vertically.
Update the App component’s return statement to render the Scheduler Pro and AG Grid components:
return (
<div id="content" className={toggleLayout ? '' : 'b-side-by-side'}>
<div className="scheduler-container">
<BryntumSchedulerPro
ref={schedulerRef}
{...schedulerConfig}
project={projectConfig}
/>
</div>
<BryntumSplitter/>
<div className="grid-container">
<div style={{ padding : '6px', borderBottom : '1px solid #ddd' }}>
<h3 style={{ fontSize : '14px', fontWeight : 'bold' }}>Unplanned Tasks (AG Grid)</h3>
<p style={{ margin : '4px 0 0 0', fontSize : '12px', color : '#666' }}>Drag tasks to the scheduler to assign them</p>
</div>
<UnplannedTasksGrid
/>
</div>
</div>
);The BryntumSplitter component splits the screen into two panels, which you can resize by dragging the splitter.
Add a Scheduler toolbar
Next, let’s create a toolbar to allow users to change time spans, navigate between dates, and toggle the layout orientation.
Create a SchedulerToolbar.tsx file in the src/components folder and add the following lines of code to it:
import { forwardRef, useCallback, type RefObject, useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { BryntumSchedulerPro, BryntumToolbar } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro-react';
import { DateHelper, Model, SchedulerPro } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
type SchedulerToolbarProps = {
schedulerRef: RefObject<BryntumSchedulerPro>
toggleLayout: boolean
setToggleLayout: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>
}
const SchedulerToolbar = forwardRef<BryntumToolbar, SchedulerToolbarProps>((props, schedulerToolbarRef) => {
const startHour = 7;
const endHour = 20;
const {
schedulerRef,
toggleLayout,
setToggleLayout
} = props;
const [scheduler, setScheduler] = useState<SchedulerPro>();
useEffect(() => {
setScheduler(schedulerRef.current!.instance);
}, [scheduler, schedulerRef, schedulerToolbarRef]);
const onSelect = useCallback((event: { record: Model }) => {
const value = event.record.get('value') as number;
const startDate = DateHelper.add(DateHelper.clearTime(scheduler!.startDate), startHour, 'h');
const endDate = DateHelper.add(startDate, value - 1, 'd');
endDate.setHours(endHour);
scheduler!.viewPreset = event.record.get('preset');
scheduler!.setTimeSpan(startDate, endDate);
// reset scroll
scheduler!.scrollLeft = 0;
}, [scheduler]);
const onShiftPrevious = useCallback(() => {
scheduler!.shiftPrevious();
}, [scheduler]);
const onShiftNext = useCallback(() => {
scheduler!.shiftNext();
}, [scheduler]);
const onClickToday = useCallback(() => {
const startDate = DateHelper.clearTime(new Date());
scheduler!.setTimeSpan(DateHelper.add(startDate, startHour, 'h'), DateHelper.add(startDate, endHour, 'h'));
}, [scheduler]);
const onToggleLayout = useCallback(() => {
setToggleLayout(!toggleLayout);
}, [setToggleLayout, toggleLayout]);
return <BryntumToolbar
ref={schedulerToolbarRef}
items={[
{
type : 'combo',
ref : 'preset',
editable : false,
label : 'Show',
value : 1,
valueField : 'value',
displayField : 'name',
items : [
{
name : '1 day',
value : 1,
preset : {
base : 'hourAndDay',
tickWidth : 45
}
},
{
name : '3 days',
value : 3,
preset : {
base : 'dayAndWeek'
}
},
{
name : '1 week',
value : 7,
preset : {
base : 'dayAndWeek'
}
}
],
onSelect
},
'->',
{
type : 'buttonGroup',
items : [
{
icon : 'b-icon b-fa-chevron-left',
cls : 'b-transparent',
onAction : onShiftPrevious
},
{
type : 'button',
text : 'Today',
cls : 'b-transparent',
onAction : onClickToday
},
{
icon : 'b-icon b-fa-chevron-right',
cls : 'b-transparent',
onAction : onShiftNext
}
]
},
'->',
{
icon : 'b-fa b-fa-columns',
tooltip : 'Toggle layout',
cls : 'b-transparent',
ref : 'toggle-layout', // for testing purpose
toggleable : true,
onAction : onToggleLayout,
style : 'margin-left: auto'
}
]}
/>;
});
SchedulerToolbar.displayName = 'SchedulerToolbar';
export default SchedulerToolbar;The SchedulerToolbar component accepts props for the scheduler ref and the toggle layout state.
The toolbar includes:
- A dropdown for selecting different time spans (
1 day,3 days, and1 week) - Navigation buttons for moving between days
- A toggle layout button
The onSelect function changes the scheduler’s time span and view preset. The onShiftPrevious and onShiftNext functions navigate between time periods, and the onClickToday function sets the date to the current date. The onToggleLayout function switches between the side-by-side layout and the stacked layout.
Now add the toolbar to the App component. Add the following imports to the App.tsx file:
import { type RefObject } from 'react';
import SchedulerToolbar from './components/SchedulerToolbar';
import { BryntumToolbar } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro-react';Add the following ref to the App component:
const schedulerToolbarRef = useRef<BryntumToolbar>(null);Render the toolbar just above the BryntumSchedulerPro component:
<SchedulerToolbar
ref={schedulerToolbarRef}
schedulerRef={schedulerRef as RefObject<BryntumSchedulerPro>}
toggleLayout={toggleLayout}
setToggleLayout={setToggleLayout}
/>Style the Scheduler Pro
In the src/index.css file, add the following import:
@import "@bryntum/schedulerpro/schedulerpro.stockholm.css";This imports the Bryntum Stockholm theme, which is one of the five available themes for Bryntum Scheduler Pro. To create a custom theme or use multiple themes, check out the Bryntum Scheduler Pro styling documentation.
Add the following styles for the AG Grid and the Scheduler Pro to the src/App.css file:
.b-sch-event {
box-shadow: 0 1px 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, .25);
}
#content {
display: flex;
flex: 1 1 100%;
}
#content:not(.b-side-by-side) {
flex-direction: column;
}
#content:not(.b-side-by-side) .scheduler-container {
order: 0;
}
#content:not(.b-side-by-side) .b-splitter {
order: 1;
}
#content:not(.b-side-by-side) .grid-container {
order: 2;
}
#content.b-side-by-side .b-grid-header {
height: 57px;
}
.scheduler-container,
.grid-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.scheduler-container > :first-child,
.grid-container > :first-child {
flex: 0 0 auto;
}
.scheduler-container {
flex: 1 1 0;
min-width: 8em;
}
.grid-container {
flex: 0 1 450px;
min-width: 1em;
}
.b-toolbar {
height: 4em;
}
.b-theme-material .b-toolbar {
height: 5em;
}
.b-filter-bar-compact .b-filter-bar-field .b-field-inner input:not(:focus)::placeholder {
color: #aaa;
}
.b-filter-bar-compact .b-filter-bar-field .b-fieldtrigger.b-fa-filter {
display: flex;
margin: 0 0.5em;
order: -1;
}
.b-resource-info .b-resource-avatar {
margin-inline-end: 1em;
width: 3em;
height: 3em;
}
.b-resource-info dl {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
flex-direction: column;
}
.b-resource-info dt {
font-weight: bold;
}
.b-resource-info .b-resource-meta {
margin-top: 0.3em;
}
.b-resource-info .b-resource-meta i {
margin-inline-end: 0.5em;
}
.b-unplannedgrid .b-de-content {
gap: 0;
}
.b-unplannedgrid .b-grid-cell i {
margin-inline-end: 0.5em;
}
.b-unplannedgrid .b-fa-clock {
margin-inline-end: 0;
}
.b-unplannedgrid .name-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
margin-inline-start: 0.3em;
}
.patient-name {
font-size: 0.8em;
margin-top: 0.2em;
}
.b-drag-proxy {
opacity: 1;
}
.b-drag-proxy .b-unassigned-class {
pointer-events: none;
transform: none;
}
.b-drag-proxy .b-unassigned-class:first-child {
z-index: 100;
}
.b-drag-proxy .b-unassigned-class .b-sch-event {
opacity: 1;
background: green;
border-color: darkgreen;
box-shadow: 0 1px 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, .25);
margin: 5px 0;
}
.b-drag-proxy.b-drag-invalid .b-sch-event {
background: red;
border-color: darkred;
}
.b-aborting.b-unassigned-class {
transition: transform 0.3s;
background: red;
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.8;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.b-sch-event-content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
font-size: 15px;
}
.b-sch-event-content i {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
}
.b-sch-event-content > span {
font-size: .8em;
font-style: italic;
}
.b-sch-highlighted-calendar-range {
animation: fadein 0.5s;
}
[data-assignment-id*="_generated"] .sch-event {
opacity: 0.4;
filter: grayscale(1);
}
@keyframes fadein {
0% {
opacity: 0;
}
100% {
opacity: 1;
}
}
.ag-row .ag-cell {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
line-height: normal;
padding: 0;
}
.ag-cell-not-inline-editing div {
padding-left: 1em;
}
.ag-cell div {
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
white-space: nowrap;
min-width: 0;
}
.ag-cell span {
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
white-space: nowrap;
min-width: 0;
}
.ag-row-group {
background-color: #fafbfc;
}
.ag-root-wrapper {
border-radius: 0;
border: none;
}Run the local development server:
npm run devYou should see one scheduled appointment:
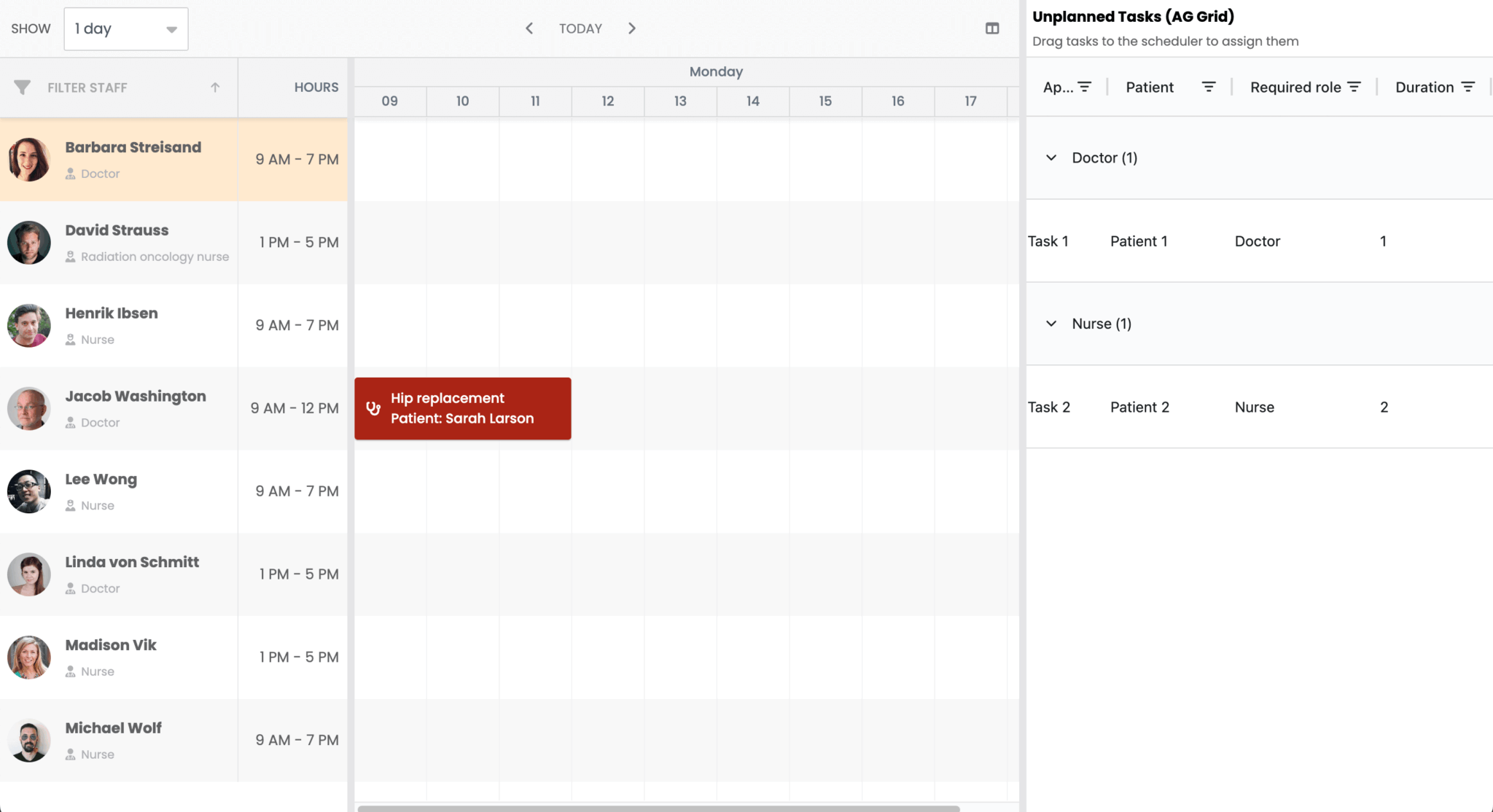
The Scheduler Pro uses the Express backend API endpoints, /api/load and api/sync, to load data into the scheduler and sync data changes to the database.
Now let’s add a drag-and-drop functionality that allows users to drag unplanned appointments from the AG Grid into the Bryntum Scheduler Pro. We’ll also improve the styling of the AG Grid rows.
Add drag-and-drop for moving unplanned tasks from the AG Grid to the Bryntum Scheduler Pro
Here, we’ll implement the core drag-and-drop functionality so that users can drag unplanned appointments across components. We’ll also create a custom drag helper for managing the drag operation, validating drop targets, and handling data transfer between components, and then use the Bryntum DragHelper class to simplify the drag-and-drop implementation.
Create a utils folder in the src folder. Create an appointmentDragHelper.ts file in src/utils and add the following lines of code to it:
import { DragHelper, StringHelper, DateHelper, SchedulerPro } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
import type { GridApi } from 'ag-grid-community';
import type { Appointment } from '../lib/Appointment';
import { Doctor } from '../lib/Doctor';
type DragConfig = {
scheduler: SchedulerPro;
gridApi: GridApi;
outerElement: HTMLElement;
}
type Context = { appointment: Appointment; appointments: Appointment[]; totalDuration: number };
export class AppointmentDragHelper extends DragHelper {
private scheduler: SchedulerPro;
private gridApi: GridApi;
static configurable = {
callOnFunctions : true,
autoSizeClonedTarget : false,
unifiedProxy : true,
removeProxyAfterDrop : true,
cloneTarget : true,
dropTargetSelector : '.b-timeline-subgrid',
targetSelector : '.ag-row'
};
constructor(config: DragConfig) {
super({ outerElement : config.outerElement });
this.scheduler = config.scheduler;
this.gridApi = config.gridApi;
}
} The configurable object defines the drag behavior:
- The
cloneTargetcreates a visual copy of the dragged element. - The
dropTargetSelectorspecifies where drops are allowed (the scheduler timeline). - The
targetSelectoridentifies what can be dragged (AG Grid rows).
The constructor accepts a Scheduler Pro instance, the AG Grid API, and the outer element containing the draggable items.
Next, add the createProxy method to the class:
createProxy(grabbedElement: HTMLElement) {
const rowId = grabbedElement.getAttribute('row-id');
const rowNode = this.gridApi.getRowNode(rowId || '');
const appointment = rowNode?.data as Appointment;
if (!appointment) return document.createElement('div');
const durationInPixels = this.scheduler.timeAxisViewModel.getDistanceForDuration(
appointment.duration * 60 * 60 * 1000
);
const proxy = document.createElement('div');
Object.assign(proxy.style, {
width : `${durationInPixels}px`,
maxWidth : `${this.scheduler.timeAxisSubGrid.width}px`,
height : `${this.scheduler.rowHeight - 2 * (this.scheduler.resourceMargin as number)}px`
});
proxy.classList.add('b-sch-event-wrap', 'b-sch-style-border', 'b-unassigned-class', 'b-sch-horizontal');
proxy.innerHTML = `
<div class="b-sch-event b-has-content b-sch-event-withicon">
<div class="b-sch-event-content">
<i class="b-icon b-fa-${appointment.iconCls}"></i>
<div>
<div>${StringHelper.encodeHtml(appointment.name)}</div>
<div class="patient-name">Patient: ${StringHelper.encodeHtml(appointment.patient || '')}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
`;
this.context.appointment = appointment;
this.context.totalDuration = appointment.duration;
return proxy;
}The createProxy method creates the visual representation of appointments during drag operations. It retrieves the appointment data from the AG Grid row, calculates the width based on the specific appointment duration, and creates an HTML element styled to look like a Scheduler Pro event.
The method uses the Scheduler Pro timeAxisViewModel to convert the appointment duration into pixels, so that the proxy matches the scheduler’s time scale. The proxy includes the appointment name, patient information, and styling, so that it matches the appearance of Scheduler Pro events.
Now, add the onDragStart method to the class:
onDragStart({ context }: { context: Context }) {
const appointment = context.appointment;
context.appointments = [appointment];
this.scheduler.enableScrollingCloseToEdges(this.scheduler.timeAxisSubGrid);
this.scheduler.features.eventTooltip.disabled = true;
// Highlight available resources
const { calendarHighlight } = this.scheduler.features;
if (calendarHighlight && appointment.requiredRole) {
const availableResources = this.scheduler.resourceStore.query((resource: Doctor) =>
resource.role === appointment.requiredRole || !appointment.requiredRole
);
calendarHighlight.highlightResourceCalendars(availableResources as Doctor);
}
}The onDragStart method initializes the drag operation by storing the appointment in the context and preparing the scheduler for the drag interaction. It enables edge scrolling, which automatically scrolls the timeline when the user drags an appointment near the left or right edge of the scheduler’s timeline, allowing users to drop appointments outside the currently visible time range.
This method also activates the calendar highlight feature to visually indicate which employees are available for the appointment based on their role.
Next, add the onDrag method to the class:
onDrag({ context }: { context: Context }) {
const { appointments, totalDuration } = context;
const requiredRole = appointments[0].requiredRole;
const newStartDate = this.scheduler.getDateFromCoordinate(context.newX, 'round', false);
const lastAppointmentEndDate = newStartDate && DateHelper.add(newStartDate, totalDuration, appointments[0].durationUnit);
const doctor = context.target && this.scheduler.resolveResourceRecord(context.target);
const calendar = doctor?.effectiveCalendar;
context.valid = Boolean(
newStartDate &&
(!requiredRole || doctor?.role === requiredRole) &&
(this.scheduler.allowOverlap || this.scheduler.isDateRangeAvailable(newStartDate, lastAppointmentEndDate, null, doctor)) &&
(!calendar || calendar.isWorkingTime(newStartDate, lastAppointmentEndDate))
);
context.doctor = doctor;
}This method performs real-time validation as the user drags the appointment over the scheduler. It calculates the proposed start time from the mouse position, determines the target employee, and checks whether the drop is valid according to these criteria:
- The appointment must have a valid start time.
- The target employee’s role must match the appointment’s required role (if specified).
- There must be no scheduling conflicts
- The proposed time must fall within the employee’s working hours, according to their calendar.
Now, add the onDrop method to the class:
async onDrop({ context }: { context: Context }) {
if (context.valid) {
const { appointments, doctor } = context;
const dropDate = this.scheduler.getDateFromCoordinate(context.newX, 'round', false);
if (!dropDate || !doctor) return;
try {
for (let i = 0; i < appointments.length; i++) {
const appointment = appointments[i];
const { project } = this.scheduler;
await this.scheduler.scheduleEvent({
eventRecord : project.eventStore.getById(appointment.id),
startDate : i === 0 ? dropDate : appointments[i - 1].endDate,
resourceRecord : doctor
});
// Remove from AG Grid
const gridRowNode = this.gridApi.getRowNode(appointment.id.toString());
if (gridRowNode?.data) {
this.gridApi.applyTransaction({ remove : [gridRowNode.data] });
}
}
}
catch (error) {
console.error('Error scheduling event:', error);
}
}
// Cleanup
const { calendarHighlight } = this.scheduler.features;
if (calendarHighlight) {
calendarHighlight.unhighlightCalendars();
}
this.scheduler.disableScrollingCloseToEdges(this.scheduler.timeAxisSubGrid);
this.scheduler.features.eventTooltip.disabled = false;
}When a valid drop occurs, the onDrop method handles the final step of scheduling an appointment by:
- Retrieving the drop coordinates
- Converting the coordinates to a date
- Updating the event in the Scheduler Pro project store
- Assigning the appointment to the target employee at a specified time
Once the appointment is scheduled, the appointment is removed from the AG Grid using the AG Grid transaction API, completing the transfer from unplanned to scheduled. The cleanup section restores the normal UI state by disabling calendar highlights, turning off edge scrolling, and re-enabling tooltips.
Now, add the following feature to the schedulerConfig in the AppConfig.ts file to enable drag validation in the Scheduler Pro:
eventDragFeature : {
validatorFn({ eventRecords, newResource, startDate, endDate }) {
const task = eventRecords[0] as Appointment;
const doctor = newResource as Doctor;
const { calendar } = doctor;
const valid = doctor.role === task.requiredRole && (!calendar || (typeof calendar !== 'string' && calendar.isWorkingTime(startDate, endDate)));
const message = valid ? '' : 'No available slot';
return {
valid,
message : (valid ? '' : '<i class="b-icon b-fa-exclamation-triangle"></i>') + message
};
}
},Add the following imports to the App.tsx file:
import { useCallback } from 'react';
import { SchedulerResourceModel } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
import type { Appointment } from './lib/Appointment';
import { Doctor } from './lib/Doctor';Add the following functions to the App component:
const onSchedulerSelectionChange = useCallback(() => {
const selectedRecords = scheduler!.selectedRecords as SchedulerResourceModel[];
const { calendarHighlight } = scheduler!.features;
if (selectedRecords.length > 0) {
calendarHighlight.highlightResourceCalendars(selectedRecords);
}
else {
calendarHighlight.unhighlightCalendars();
}
}, [scheduler]);
const onGridSelectionChange = useCallback((selectedRecords: Appointment[]) => {
if (!scheduler) return;
const { calendarHighlight } = scheduler.features;
const requiredRoles: Record<string, number> = {};
selectedRecords.forEach((appointment: Appointment) => requiredRoles[appointment.requiredRole as string] = 1);
if (Object.keys(requiredRoles).length === 1) {
const appointment = selectedRecords[0];
const availableResources = scheduler.resourceStore
.query((doctor: Doctor) => doctor.role === appointment.requiredRole || !appointment.requiredRole) as SchedulerResourceModel[];
calendarHighlight.highlightResourceCalendars(availableResources);
}
else {
calendarHighlight.unhighlightCalendars();
}
}, [scheduler]);These functions highlight the available employees for any appointment selected by the user in the Scheduler Pro or the AG Grid.
Add the following prop to the BryntumSchedulerPro component:
onSelectionChange={onSchedulerSelectionChange}Add the following props to the UnplannedTasksGrid component:
<UnplannedTasksGrid
scheduler={scheduler}
onSelectionChange={onGridSelectionChange}
/>Now we need to update the UnplannedTasksGrid component to add the unassigned Scheduler Pro appointment data to the AG Grid and to enable the drag-and-drop functionality. We’ll transform the AG Grid from a display of hardcoded data to a fully integrated component that synchronizes with the Scheduler Pro project data.
Add the following imports to the UnplannedTasksGrid.tsx file:
import { useCallback, useEffect } from 'react';
import { type GetRowIdParams, type SelectionChangedEvent, type GridReadyEvent, type GridApi } from 'ag-grid-community';
import type { Appointment } from '../lib/Appointment';
import { useUnplannedTasks } from '../hooks/useUnplannedTasks';
import { AppointmentDragHelper } from '../utils/appointmentDragHelper';Destructure the scheduler and onSelectionChange props from the UnplannedTasksGrid component:
- export const UnplannedTasksGrid = () => {
+ export const UnplannedTasksGrid = ({ scheduler, onSelectionChange }) => {Add the following refs and custom hook call, which we’ll soon define, to the UnplannedTasksGrid component:
const gridApiRef = useRef<GridApi | null>(null);
const dragHelperRef = useRef<AppointmentDragHelper | null>(null);
const { tasks, loading, error } = useUnplannedTasks(scheduler);Delete the existing hardcoded tasks state:
- const [tasks] = useState([
- ...Add the following initializeDragHelper function to the UnplannedTasksGrid component:
const initializeDragHelper = useCallback(() => {
if (!scheduler || !gridApiRef.current) return;
const gridElement = document.querySelector('.ag-grid-container') as HTMLElement;
if (!gridElement) return;
// Clean up existing drag helper before creating a new one
dragHelperRef.current?.destroy();
dragHelperRef.current = new AppointmentDragHelper({
scheduler,
gridApi : gridApiRef.current,
outerElement : gridElement
});
// Return cleanup function
return () => dragHelperRef.current?.destroy();
}, [scheduler]);This function initializes the drag helper by creating a new AppointmentDragHelper instance with the Scheduler Pro, AG Grid API, and AG Grid container element.
Add the following handleUpdateEvent function to the UnplannedTasksGrid component:
const handleUpdateEvent = useCallback((eventId: number, updates: Partial<Appointment>) => {
if (!scheduler?.project?.eventStore) return;
const event = scheduler.project.eventStore.getById(eventId);
if (event) {
// Apply updates to the Bryntum event record
// This will trigger auto-sync due to autoSync: true in project config
Object.assign(event, updates);
}
}, [scheduler]);This function updates the appointment in the Scheduler Pro when the user edits the corresponding appointment in the AG Grid. Then, because of the autoSync: true setting in the project config, it automatically applies the updates to the Bryntum event record.
Add the following effect hook below the initializeDragHelper function:
useEffect(() => {
const cleanup = initializeDragHelper();
return cleanup;
}, [initializeDragHelper]);This effect hook initializes the drag helper when the component mounts. It returns a cleanup function that destroys the drag helper when the component unmounts.
Update the columnDefs variable to use the Appointment type:
- const columnDefs: ColDef[] = [
+ const columnDefs: ColDef<Appointment>[] = [In the columnDefs 'name' field object, add the following onCellValueChanged and cellRenderer functions:
onCellValueChanged : (params) => {
handleUpdateEvent(params.data.id, { name : params.newValue });
},
cellRenderer : ({ data }: { data: Appointment }) => (
<div style={{ display : 'flex', alignItems : 'center' }}>
<i className={`b-fa b-fa-${data.iconCls}`} />
<div style={{ display : 'flex', flexDirection : 'column', justifyContent : 'center', gap : '2px', minWidth : 0, flex : 1 }}>
<span>{data.name}</span>
<span style={{ fontSize : '12px', color : '#666' }}>Patient: {data.patient}</span>
</div>
</div>
)The onCellValueChanged function updates the appointment name in the Scheduler Pro when the user edits the name in the AG Grid. The cellRenderer function is used to display the appointment name and patient information in the column cells.
Now remove the columnDefs 'patient' field object:
- {
- headerName : 'Patient',
- field : 'patient',
- width : 120,
- editable : true
- },Add the following onCellValueChanged and cellRenderer functions to the columnDefs 'requiredRole' field object:
onCellValueChanged : (params) => {
handleUpdateEvent(params.data.id, { requiredRole : params.newValue });
},
cellRenderer : ({ data }: { data: Appointment }) => (
<div>
{data.requiredRole}
</div>
)Add the following onCellValueChanged and cellRenderer functions to the columnDefs 'duration' field object:
onCellValueChanged : (params) => {
handleUpdateEvent(params.data.id, { duration : params.newValue });
},
cellRenderer : ({ data }: { data: Appointment }) => (
<div>
{data.duration} {data.durationUnit}{data.duration === 1 ? '' : 's'}
</div>
)Now, add the following functions to the UnplannedTasksGrid component:
const getRowId = useCallback((params: GetRowIdParams<Appointment>) => {
return params.data.id.toString();
}, []);
const handleSelectionChanged = useCallback((event: SelectionChangedEvent<Appointment>) => {
const selectedNodes = event.api.getSelectedNodes();
const selectedRecords = selectedNodes.map(node => node.data).filter(Boolean);
onSelectionChange?.(selectedRecords);
}, [onSelectionChange]);
const handleGridReady = useCallback((event: GridReadyEvent<Appointment>) => {
gridApiRef.current = event.api;
initializeDragHelper();
}, [initializeDragHelper]);The getRowId function returns the appointment ID as a string. The handleSelectionChanged function calls the onSelectionChange function, which calls the onGridSelectionChange function in the App.tsx file.
This function highlights the available time slots in the Scheduler Pro when the user selects an appointment in the AG Grid.
The handleGridReady function initializes the drag helper when the grid is ready.
Add the following code to the UnplannedTasksGrid component below the handleGridReady function:
if (loading) return <div>Loading tasks...</div>;
if (error) return <div>Error: {error}</div>;This code checks whether the tasks are loading or there has been an error, and displays a loading or error message.
Add the functions we just defined as props to the AgGridReact component:
getRowId={getRowId}
onSelectionChanged={handleSelectionChanged}
onGridReady={handleGridReady}Let’s also decrease the row height to 45px for group rows and 65px for other rows to make the grid more compact:
- rowHeight={80}
+ getRowHeight={params => params.node.group ? 45 : 65}Now let’s create the custom React Hook that gets the unassigned tasks for the AG Grid and add CRUD event listeners to the Scheduler Pro project.
Create a custom React Hook to get unassigned tasks for the AG Grid and to add CRUD event listeners to the Scheduler Pro project
To keep the AG Grid synchronized with the Scheduler Pro data, we’ll use a custom React Hook to listen for changes in the Scheduler Pro project data and automatically update the AG Grid when appointments are added, removed, or modified.
The hook filters the Scheduler Pro event store to find appointments that don’t have any resource assignments, in other words, unplanned appointments. It also sets up event listeners to react to changes in both the event store and assignment store, ensuring the AG Grid stays synchronized with the Scheduler Pro data.
Create a hooks folder in the src folder and create a useUnplannedTasks.ts file in it.
Add the following imports and type definitions to src/hooks/useUnplannedTasks.ts:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import type { AssignmentModel, AssignmentStore, EventColor, EventStore, Model, SchedulerPro } from '@bryntum/schedulerpro';
import type { Appointment } from '../lib/Appointment';
interface UnplannedTask {
id: string | number;
name: string;
iconCls: string;
patient: string;
confirmed: boolean;
duration: number;
eventColor: EventColor;
requiredRole: string;
durationUnit: string;
}
interface UseUnplannedTasksResult {
tasks: UnplannedTask[];
loading: boolean;
error: string | null;
}Now, add the following useUnplannedTasks function:
export const useUnplannedTasks = (scheduler?: SchedulerPro): UseUnplannedTasksResult => {
const [tasks, setTasks] = useState<UnplannedTask[]>([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [error, setError] = useState<string | null>(null);
return { tasks, loading, error };
};This hook has three pieces of state:
- A
tasksarray containing unplanned appointments - A
loadingflag - An
errorstate for displaying errors
Add the following useEffect hook to the useUnplannedTasks function:
// Listen for scheduler project data changes
useEffect(() => {
if (!scheduler?.project) {
setLoading(true);
return;
}
const updateTasks = () => {
try {
const formattedTasks = formatUnplannedEvents(
scheduler.project.eventStore,
scheduler.project.assignmentStore
);
setTasks(formattedTasks);
setError(null);
setLoading(false);
}
catch (err) {
setError(err instanceof Error ? err.message : 'Failed to update tasks');
setLoading(false);
}
};
// Initial load when project is ready
if (scheduler.project.eventStore && scheduler.project.assignmentStore) {
updateTasks();
}
// Listen to store changes for automatic updates
const eventStoreListeners = {
add : updateTasks,
remove : updateTasks,
update : updateTasks,
change : updateTasks
};
const assignmentStoreListeners = {
add : updateTasks,
remove : updateTasks,
change : updateTasks
};
// Add listeners
Object.entries(eventStoreListeners).forEach(([event, handler]) => {
scheduler.project.eventStore.on(event, handler);
});
Object.entries(assignmentStoreListeners).forEach(([event, handler]) => {
scheduler.project.assignmentStore.on(event, handler);
});
// Listen for project load completion
scheduler.project.on('load', updateTasks);
// Cleanup listeners
return () => {
Object.entries(eventStoreListeners).forEach(([event, handler]) => {
scheduler.project.eventStore.un(event, handler);
});
Object.entries(assignmentStoreListeners).forEach(([event, handler]) => {
scheduler.project.assignmentStore.un(event, handler);
});
scheduler.project.un('load', updateTasks);
};
}, [scheduler]);The useEffect hook syncs data changes between the Scheduler Pro and the AG Grid. The updateTasks function filters the event store to find unplanned appointments for the AG Grid. Event listeners for the event and assignment stores use the updateTasks function to update the AG Grid tasks state when appointments are scheduled, unscheduled, or modified.
Finally, add the following formatUnplannedEvents function to the useUnplannedTasks function:
const formatUnplannedEvents = (eventStore: EventStore, assignmentStore: AssignmentStore) => {
if (!eventStore || !assignmentStore) return [];
const unplannedEvents = eventStore.records.filter((event: Model) => {
// Check if event has any assignments
const hasAssignments = (assignmentStore.records as AssignmentModel[]).some((assignment) =>
assignment.eventId === event.id || assignment.event === event.id
);
return !hasAssignments;
});
return (unplannedEvents as Appointment[]).map((event) => ({
id : event.id,
name : event.name,
iconCls : event.iconCls?.replace('b-fa b-fa-', '') || event.iconCls?.replace('b-icon b-fa-', '') || 'stethoscope',
patient : event.patient || '',
confirmed : event.confirmed,
duration : event.duration || 1,
eventColor : event.eventColor,
requiredRole : event.requiredRole || 'Other',
durationUnit : event.durationUnit || 'h'
})).sort((a, b) => a.requiredRole.localeCompare(b.requiredRole));
};This helper function filters the event store to find events that don’t have corresponding entries in the assignment store, which indicates they haven’t been assigned to any employee. The unplanned events are then formatted for the AG Grid. The results are sorted by required role, so that similar appointments are grouped together in the grid.
Run the frontend and backend development servers. You’ll now be able to drag appointments from the AG Grid to the Scheduler Pro. You’ll only be able to drop events in the slots available for employees with the required roles.
Next steps
We created a basic AG Grid and Bryntum Scheduler Pro integration with drag-and-drop capabilities. Here are some ideas for improving the app:
- Add additional appointment fields: The basic integration supports persisting some common data model fields and the custom fields (
patient,requiredRole,confirmed,role, androleIconCls). You can add support for additional appointment fields (such as effort, completion percentages, and notes) and configure the task editor to display the custom fields. View an example in the Bryntum task editor demo. - Add create and delete functionality to the AG Grid: You can add Create and Delete buttons to the AG Grid.
- Add automatic cleanup of orphaned dependencies: You can remove event dependencies when they are unscheduled.